Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs) are a type of insecticide that break the insect life cycle by interfering with growth and development. Simply put, the insect fails to properly grow into a mature adult. Some IGRs are targeted to specific pests, while others will be effective on many species.
IGRs will often not kill the target pest, but can leave visible side effects, such as twisted wings. Other effects of IGRs can include reduced egg hatch and reduced fecundity in the adult. IGRs primarily impact immatures and will not kill adult insects. Therefore, it is important to apply IGRs in such a way that immatures will be exposed to them.
Many PMPs like to combine IGRs with adulticides to incorporate multiple modes of action and address the adult population. IGRs are a popular choice as many are considered reduced impact on vertebrates.
What are the different types of IGRs?
Hormone Mimics
Molting is a complex process. A lot of things must happen at the right time and in the right order for a molt to be successful. Depending on hormone levels, an immature insect will either molt to the next instar, pupa, or adult. One of those hormones is juvenile hormone (JH).
Common IGRs, such as pyriproxyfen, hydroprene, and methoprene, are juvenile hormone mimics (JHM). Insects exposed to these products experience an unnatural surge in JH, resulting in incorrect development.
Chitin Synthesis Inhibitors
Insects do not have an internal skeleton like people do. Their skeleton is on the outside. This exoskeleton is largely made of chitin. Chitin is a fibrous polymer, comparable to keratin (the protein that makes up hair, nails, and horns in vertebrates).
Immature insects have to shed their old exoskeleton to grow. Immediately after molting, the insect is soft and vulnerable. After some time, the exoskeleton will harden again. When exposed to chitin synthesis inhibitors (such as noviflumuron), this process is disrupted, and the insect cannot properly form its new exoskeleton. Without this structure in place, the insect will die.
Other Molting Disruptors
Molting disruptors, such as cyromazine, do exactly like their name suggests. They are similar to chitin synthesis inhibitors but have a different mode of action. These tend to be very specific to their target pest.
Choosing the Right IGR
PMPs have several options when choosing an IGR product. Compare several popular IGR products, including MGK’s NyGuard® to find the one that is right for you.
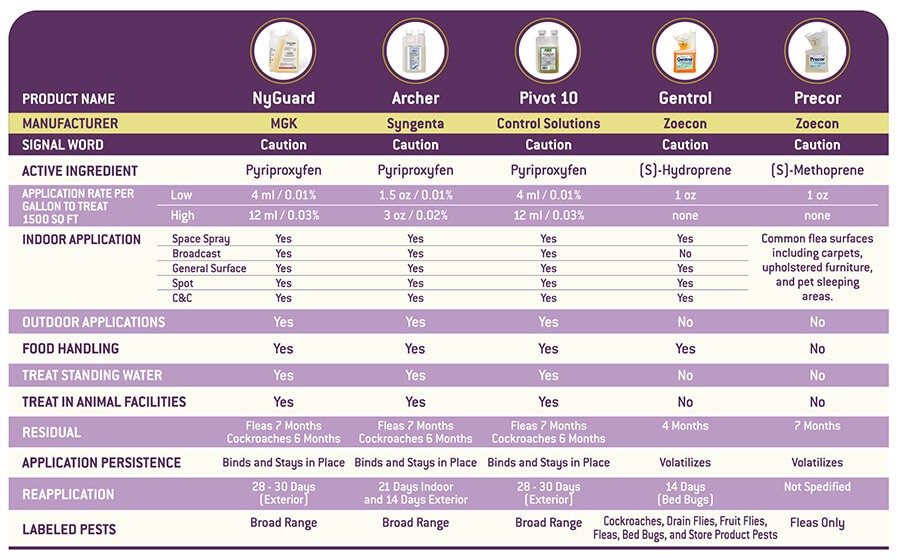
Additional Resources:
- Learn more about IGRs in Issue 8 of MGK’s PMP Pulse Newsletter
- Get a comprehensive technical overview of IGRs on our blog

